| Unity动画TA:一些算法 Cheat Sheet | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › numpy 连乘 › Unity动画TA:一些算法 Cheat Sheet |
Unity动画TA:一些算法 Cheat Sheet
|
备忘录,可能持续更新。 位移、旋转、缩放转矩阵实现与Matrix4x4自带同名方法相同的效果 public static Matrix4x4 Rotate(Quaternion q) { q.Normalize(); float q_x = q.x, q_y = q.y, q_z = q.z, q_w = q.w; float x2 = q_x * q_x, y2 = q_y * q_y, z2 = q_z * q_z; float xy = q_x * q_y, xz = q_x * q_z, yz = q_y * q_z, xw = q_x * q_w, yw = q_y * q_w, zw = q_z * q_w; Matrix4x4 rotMat = new Matrix4x4( new Vector4(1 - 2 * y2 - 2 * z2, 2 * xy + 2 * zw, 2 * xz - 2 * yw, 0), new Vector4(2 * xy - 2 * zw, 1 - 2 * x2 - 2 * z2, 2 * yz + 2 * xw, 0), new Vector4(2 * xz + 2 * yw, 2 * yz - 2 * xw, 1 - 2 * x2 - 2 * y2, 0), new Vector4(0, 0, 0, 1)); return rotMat; } public static Matrix4x4 Translate(Vector3 t) { Matrix4x4 transMat = new Matrix4x4(new Vector4(1,0,0,0), new Vector4(0,1,0,0), new Vector4(0,0,1,0), new Vector4(t.x, t.y, t.z,1)); return transMat; } public static Matrix4x4 Scale(Vector3 s) { Matrix4x4 scaleMat = new Matrix4x4(new Vector4(s.x, 0, 0, 0), new Vector4(0, s.y, 0, 0), new Vector4(0, 0, s.z, 0), new Vector4(0, 0, 0, 1)); return scaleMat; } public static Matrix4x4 TRS(Vector3 t, Quaternion r, Vector3 s) { Matrix4x4 trs = Rotate(r) * Scale(s); trs.SetColumn(3, new Vector4(t.x, t.y, t.z, 1)); return trs; //return Translate(t) * Rotate(r) * Scale(s); } Cubic Hermite Curve用矩阵实现 /// /// Cubic Hermite2D,实际上把Vector2类型的参数换成Vector3就是Hermite3D /// /// 参数t /// 第一个点 /// 第二个点 /// 第一个点切线 /// 第二个点切线 /// public static Vector4 Hermite2D(float t, Vector2 P1 ,Vector2 P2, Vector2 T1, Vector2 T2) { //永远不变的矩阵,应该提到外面去写成readonly Matrix4x4 H = new Matrix4x4(new Vector4(1, 0, 0, 0), new Vector4(0, 0, 1, 0), new Vector4(-3, 3, -2, -1), new Vector4(2, -2, 1, 1)); //每条Hermite只需要计算一次,应该搬到外边 Matrix4x4 P = new Matrix4x4(P1, P2, T1, T2); float t_2 = t * t; float t_3 = t_2 * t; Vector4 T = new Vector4(1, t, t_2, t_3); return P * H * T; } 四个2D点实现拉格朗日插值用矩阵写是为了以后迁移到python做准备。 /// /// 平面四个点做拉格朗日插值 /// /// 数据点1 /// 数据点2 /// 数据点3 /// 数据点4 /// x /// y public static float LagrangeInterpolationCubic(Vector2 xy1, Vector2 xy2, Vector2 xy3, Vector2 xy4, float x) { //跟python风格对齐的话,可以直接传入X和Y Vector4 X = new Vector4(xy1.x, xy2.x, xy3.x, xy4.x); Vector4 Y = new Vector4(xy1.y, xy2.y, xy3.y, xy4.y); Matrix4x4 X4 = new Matrix4x4(X, X, X, X); //每两个元素之间减一次,存在4x4矩阵中 Matrix4x4 X4SubX4T = MatrixSubtract(X4, X4.transpose); //把自己减自己的地方置为1 X4SubX4T = MatrixAdd(X4SubX4T, Matrix4x4.identity); Vector4 xCap = new Vector4(x, x, x, x); Vector4 cap = xCap - X; //以下计算L的部分如果用numpy还可以继续向量化 float L1 = (cap.y * cap.z * cap.w) / Prod(X4SubX4T.GetRow(0)); float L2 = (cap.x * cap.z * cap.w) / Prod(X4SubX4T.GetRow(1)); float L3 = (cap.x * cap.y * cap.w) / Prod(X4SubX4T.GetRow(2)); float L4 = (cap.x * cap.y * cap.z) / Prod(X4SubX4T.GetRow(3)); Vector4 L = new Vector4(L1, L2, L3, L4); float res = Vector4.Dot(Y, L); return res; } /// /// 所有元素连乘 /// /// X /// public static float Prod(Vector4 x) { return x.x * x.y * x.z * x.w; } /// /// 逐元素矩阵加法 /// /// 矩阵a /// 矩阵b /// a+b public static Matrix4x4 MatrixAdd(Matrix4x4 a, Matrix4x4 b) { Matrix4x4 add = new Matrix4x4(a.GetColumn(0) + b.GetColumn(0), a.GetColumn(1) + b.GetColumn(1), a.GetColumn(2) + b.GetColumn(2), a.GetColumn(3) + b.GetColumn(3)); return add; } /// /// 逐元素矩阵减法 /// /// 矩阵a /// 矩阵b /// a-b public static Matrix4x4 MatrixSubtract(Matrix4x4 a, Matrix4x4 b) { Matrix4x4 sub = new Matrix4x4(a.GetColumn(0) - b.GetColumn(0), a.GetColumn(1) - b.GetColumn(1), a.GetColumn(2) - b.GetColumn(2), a.GetColumn(3) - b.GetColumn(3)); return sub; } 以上拉格朗日插值实现的效果 以上拉格朗日插值实现的效果稍作修改得到双线性二次插值。 /// /// 双线性二次插值 /// /// 数据点1 /// 数据点2 /// 数据点3 /// 数据点4 /// x /// y public static float LagrangeInterpolationSquare(Vector2 xy1, Vector2 xy2, Vector2 xy3, Vector2 xy4, float x) { //跟python风格对齐的话,可以直接传入X和Y Vector4 X = new Vector4(xy1.x, xy2.x, xy3.x, xy4.x); //Vector4 Y = new Vector4(xy1.y, xy2.y, xy3.y, xy4.y); Matrix4x4 X4 = new Matrix4x4(X, X, X, X); //每两个元素之间减一次,存在4x4矩阵中 Matrix4x4 X4SubX4T = MatrixSubtract(X4, X4.transpose); //把自己减自己的地方置为1 X4SubX4T = MatrixAdd(X4SubX4T, Matrix4x4.identity); Vector4 xCap = new Vector4(x, x, x, x); Vector4 cap = xCap - X; //以下计算L的部分如果用numpy还可以继续向量化 float L1 = (cap.y * cap.z) / (X4SubX4T[0, 1] * X4SubX4T[0, 2]); float L2 = (cap.x * cap.z) / (X4SubX4T[1, 0] * X4SubX4T[1, 2]); float L3 = (cap.x * cap.y) / (X4SubX4T[2, 0] * X4SubX4T[2, 1]); Vector3 lPrev = new Vector3(L1, L2, L3); Vector3 yPrev = new Vector3(xy1.y, xy2.y, xy3.y); float resPrev = Vector3.Dot(lPrev, yPrev); L1 = (cap.z * cap.w) / (X4SubX4T[1, 2] * X4SubX4T[1, 3]); L2 = (cap.y * cap.w) / (X4SubX4T[2, 1] * X4SubX4T[2, 3]); L3 = (cap.y * cap.z) / (X4SubX4T[3, 1] * X4SubX4T[3, 2]); Vector3 lNext = new Vector3(L1, L2, L3); Vector3 yNext = new Vector3(xy2.y, xy3.y, xy4.y); float resNext = Vector3.Dot(lNext, yNext); float t = (x - X.y) / (X.z - X.y); return Mathf.Lerp(resPrev, resNext, t); }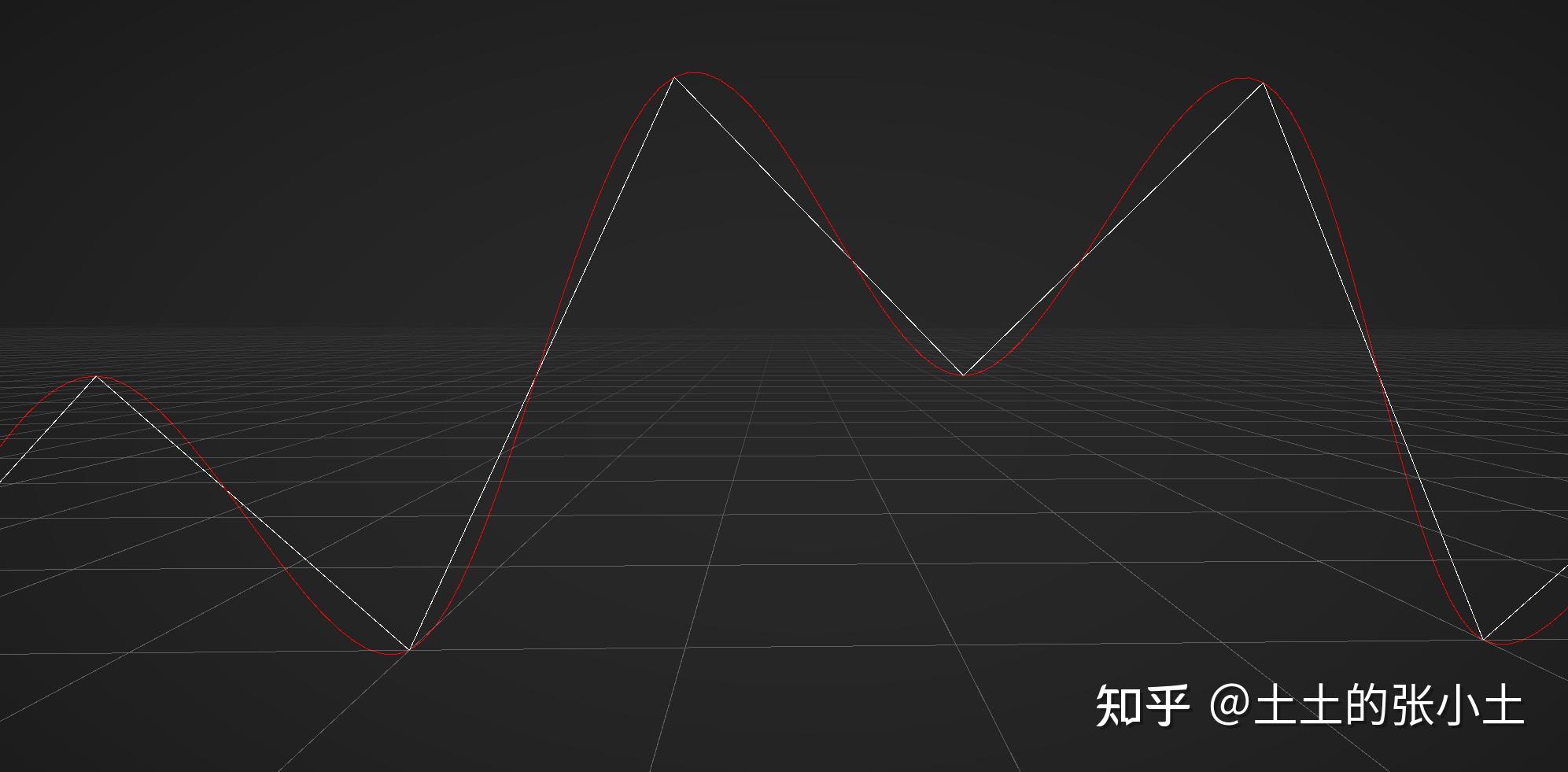 双线性二次插值 双线性二次插值
|
【本文地址】
公司简介
联系我们